Zelenskyy joins Canadian Parliament’s ovation to 98-year-old veteran who fought with Nazis
Nazis #Nazis
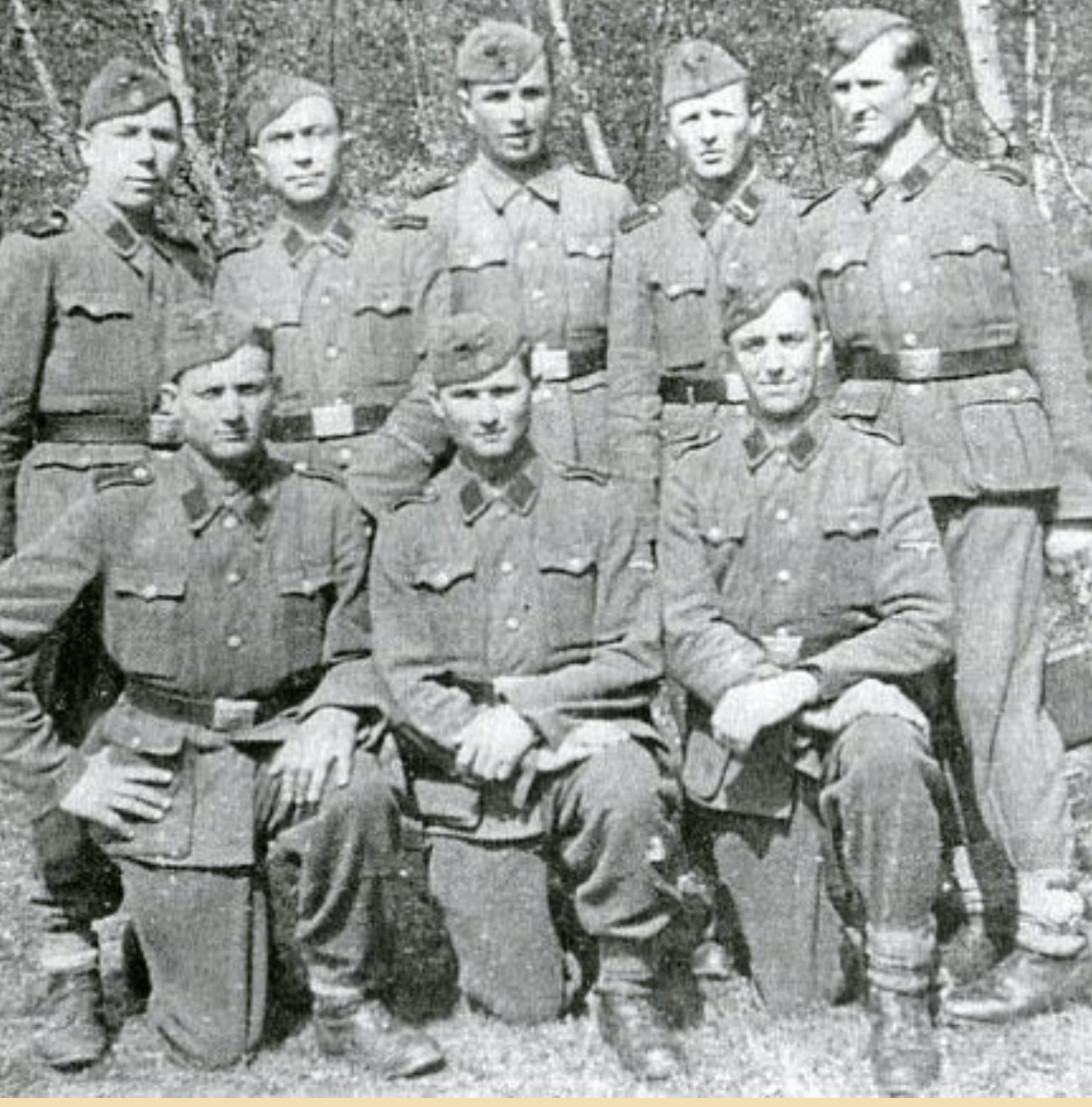


One of several photos on a blog by an SS Galichina veterans’ group that shows Yaroslav Hunka, the Ukrainian immigrant honored by the Canadian Parliament during a visit by Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy. Hunka is in the front row, middle.

By Lev Golinkin September 24, 2023
The Canadian Parliament gave a standing ovation on Friday to a 98-year-old immigrant from Ukraine who fought in a Third Reich military formation accused of war crimes.
The elderly veteran, Yaroslav Hunka was honored during a session in which President Volodomyr Zelenskyy of Ukraine addressed the lawmakers to thank them for their support since Russia invaded his country, saying Canada has always been on “the bright side of history.” The Speaker of the House of Commons, Anthony Rota — who had compared Zelenskyy to Winston Churchill — recognized a “veteran from the Second World War who fought for Ukrainian independence against the Russians and continues to support the troops today even at his age of 98.”
The assembly then rose to applaud a man in a khaki uniform standing on the balcony, who saluted, according to this screenshot from Canadian television.
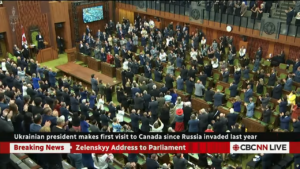
The man was identified as Hunka by the Associated Press, which published a photograph showing Zelenskyy smiling and raising a fist during the ovation.
The AP caption described Hunka as having “fought with the First Ukrainian Division in World War II before later immigrating to Canada.” The First Ukrainian Division is another name for the 14th Waffen Grenadier Division of the SS, the military wing of the Nazi Party; the unit was also called SS Galichina.
This is the same unit that is honored by controversial monuments in Canada, Australia, and, as the Forward recently exposed, the suburbs of Philadelphia and Detroit. Jewish groups have called for their removal.
After a Forward article in August that was followed by coverage in the Philadelphia Inquirer, local television stations and other news outlets, the Ukrainian Catholic Archeparchy of Philadelphia temporarily covered the monument located in a cemetery in Elkins Park, Pennsylvania, pending discussions with local Jewish leaders. The Jewish Federation of Greater Philadelphia and regional branches of the American Jewish Committee and the Anti-Defamation League had expressed outrage about the monument.
Formed in 1943, SS Galichina was composed of recruits from the Galicia region in western Ukraine. The unit was armed and trained by the Nazis and commanded by German officers. In 1944, the division was visited by SS head Heinrich Himmler, who spoke of the soldiers’ willingness to slaughter Poles.”
Three months earlier, SS Galichina subunits perpetrated what is known as the Huta Pieniacka massacre, burning 500 to 1,000 Polish villagers alive.
During the Nuremberg Trials, the International Military Tribunal declared the Waffen-SS to be a criminal organization responsible for mass atrocities including the “persecution and extermination of the Jews, brutalities and killings in concentration camps, excesses in the administration of occupied territories, the administration of the slave labor program, and the mistreatment and murder of prisoners.”
After the war, thousands of SS Galichina veterans were allowed to resettle in the West, around 2,000 of them in Canada. By then, the unit was universally known as the First Ukrainian Division.
A blog by an association of its veterans, called “Combatant News” in Ukrainian, includes an autobiographical entry by a Yaroslav Hunka that says he volunteered to join the division in 1943 and several photographs of him during the war. The captions say the pictures show Hunka during SS artillery training in Munich in December 1943 and in Neuhammer (now Świętoszów), Poland, the site of Himmler’s visit.
In posts to the blog dated 2011 and 2010, Hunka describes 1941 to 1943 as the happiest years of his life and compares the veterans of his unit, who were scattered across the world, to Jews.
Canada has two monuments to the unit, one in a Wayville, which is outside Toronto, the other in Edmonton. Canadian Jewish organizations have called for their removal.
It is unclear whether Zelenskyy knew that Hunka fought with the unit. In 2021, the Ukrainian president joined the governments of Israel and Germany in denouncing a march honoring SS Galichina in Kyiv.
Lev Golinkin is the author of A Backpack, a Bear, and Eight Crates of Vodka, Amazon’s Debut of the Month, a Barnes & Noble Discover Great New Writers program selection, and winner of the Premio Salerno Libro d’Europa. A graduate of Boston College, Golinkin came to the U.S. as a child refugee from the eastern Ukrainian city of Kharkov (now called Kharkiv) in 1990. His writing on the Ukraine crisis, Russia, the far right, and immigrant and refugee identity has appeared in The New York Times, The Washington Post, the Los Angeles Times, CNN, NBC, The Boston Globe, Politico Europe, and Time.com, among others; he has been interviewed by MSNBC, NPR, ABC Radio, WSJ Live and HuffPost Live.